Wondering what is low testosterone considered? Testosterone is a hormone that helps regulate many bodily functions, but it can also cause adverse side effects when levels are too low.
Testosterone is a hormone found in both males and females. In healthy males, testosterone is found at a concentration range of 270 ng/dL-1070n g/dL.1 Healthy testosterone levels for females should be anywhere from 15 ng/dL-70 ng/dL.1 Testosterone production occurs in the Leydig cells of the testes.2 Read on if you are looking to answer the question, “what is considered low testosterone?”

In males, testosterone is an essential component of the development of primary sexual functions and characteristics, including the descent of the testicles, enlargement of the penis and testes, and development of libido. Later in life, the role of testosterone is to regulate secondary male sex characteristics that are associated with masculinity.3
So, what is considered low testosterone?
When testosterone is used for any reason that is not medically supported, it is considered anabolic steroid misuse.4 Situations of steroid misuse are both illegal and dangerous for the individual. To ensure appropriate usage, patients considering testosterone treatment should speak with a medical professional to determine the testosterone dosage and treatment plan that will work for their situation.
Read on to learn what is considered low testosterone.
In adulthood, the purpose of testosterone is to regulate libido, help with the production of red blood cells and sperm, and maintain bone and muscle mass.6 Healthy testosterone function continues to support sexual function and masculine behaviors. When testosterone levels exceed or fall below the normal range, patients may experience undesirable effects, such as the symptoms of hypogonadism.
Read on to learn what is considered low testosterone.
Testosterone production is controlled by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland receives signals from the brain to increase or decrease testosterone production and then relays these signals to the testes.7
But what is considered low testosterone?
When it comes to considered what low testosterone is, one has to take age into account. The average levels of testosterone for men by age are:8
These levels may vary somewhat from person to person, meaning what is considered low testosterone will vary based on age. Maintaining testosterone levels within a healthy range as men continue to age is essential for continued healthy body function. Having high or low levels of testosterone can impact men in many ways, including affecting libido and overall energy levels.
What is considered low testosterone and how do you test it? There are many different tests that can measure what is considered low testosterone levels in the body, including:
The free testosterone test measures testosterone in its active form.9
Want to figure out what is considered low testosterone and how you can test for it? Free testosterone is the testosterone in the body that is not bound to proteins. Bioavailable testosterone refers to both free testosterone and testosterone bound to the protein albumin.11
What is considered low testosterone when it comes to fetal development? Low testosterone in fetal development will lead to poor development of primary sex characteristics. Features may include small testes and a small phallus. After birth and in the pre-pubertal years, the features of low testosterone may include gynecomastia, difficulty gaining muscle mass, and low energy.3
When it comes to puberty, what is considered low testosterone levels than normal?
Healthy testosterone levels in adolescents are necessary for puberty. In adolescents with delayed puberty, primary and secondary hypogonadism explain less than 20% of cases.19 The features of low testosterone in puberty and after puberty may include small testes, small phallus, gynecomastia, low sperm count, low energy, and decreased secondary sex characteristics (such as facial or axillary hair).3
In adulthood, it is essential to learn what is considered low testosterone. Hypogonadism is very common in adult males. Between 10-40% of men internationally have been diagnosed with testosterone deficiency.20 In the U.S. alone, it is estimated that four to five million men are affected by hypogonadism.21
Learn the signs of what is considered low testosterone. Some common signs of testosterone deficiency include:
Looking to answer what is considered low testosterone and how to treat low T levels? There are many treatments besides TRT that advertise ways to get testosterone levels back to normal. However, it is important that patients select a method that has been proven to produce the desired treatment results.
Testosterone replacement therapy, or TRT, is a treatment for the symptoms of hypogonadism. TRT provides the body with an external source of testosterone to bring testosterone concentrations into the healthy range. There are several studies that have proven the ability of TRT to raise testosterone concentrations. In a systematic review of 57 TRT treatment studies varying from 12 weeks to 36 months, it was found that 92.8% of treatments raised total testosterone concentrations above 346 ng/dL.25
Trying to figure out what is considered low testosterone and how to treat it?
One of the first benefits of testosterone testing is that patients will finally receive an answer for the symptoms they have been experiencing. Low libido, decreased energy, and moodiness can leave a person feeling frustrated and lonely. While being diagnosed with hypogonadism may feel challenging, the good news is that hypogonadal patients will have the opportunity to treat their symptoms and start to feel like themselves again.
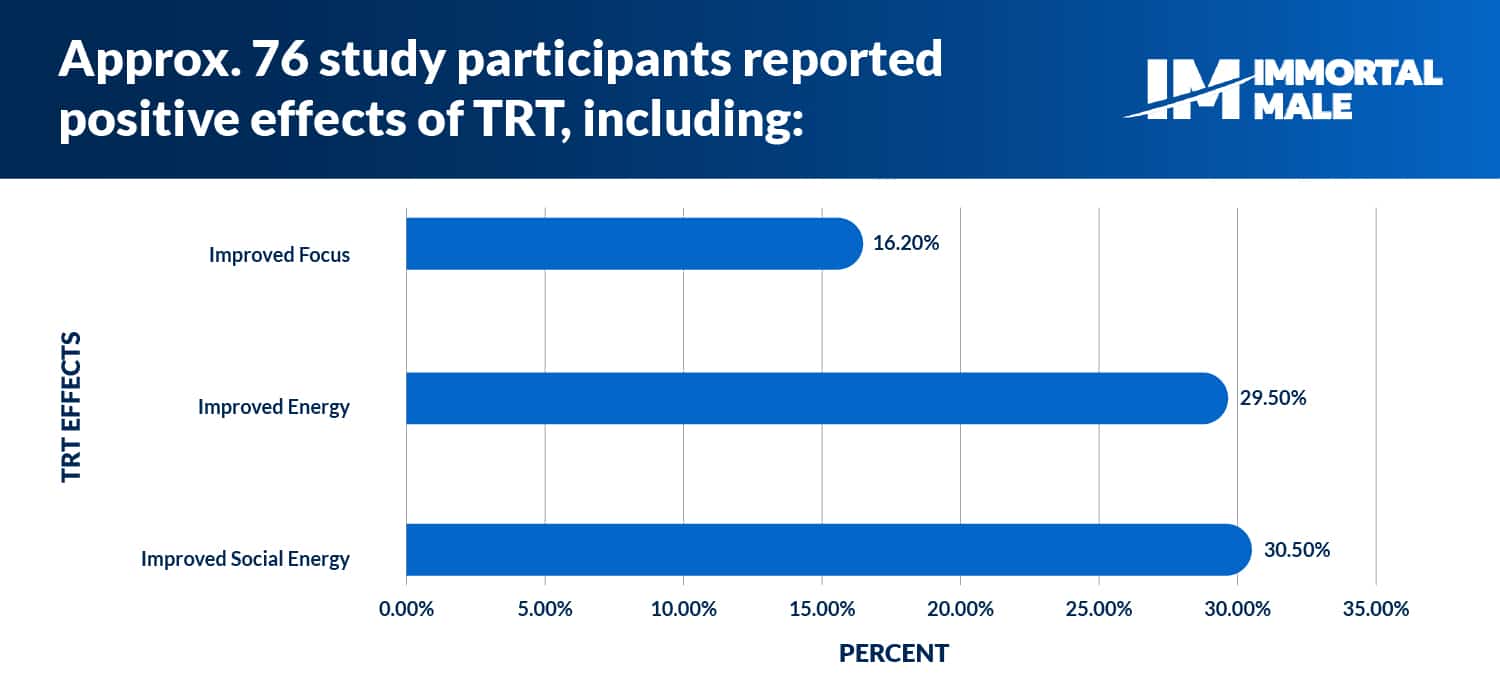
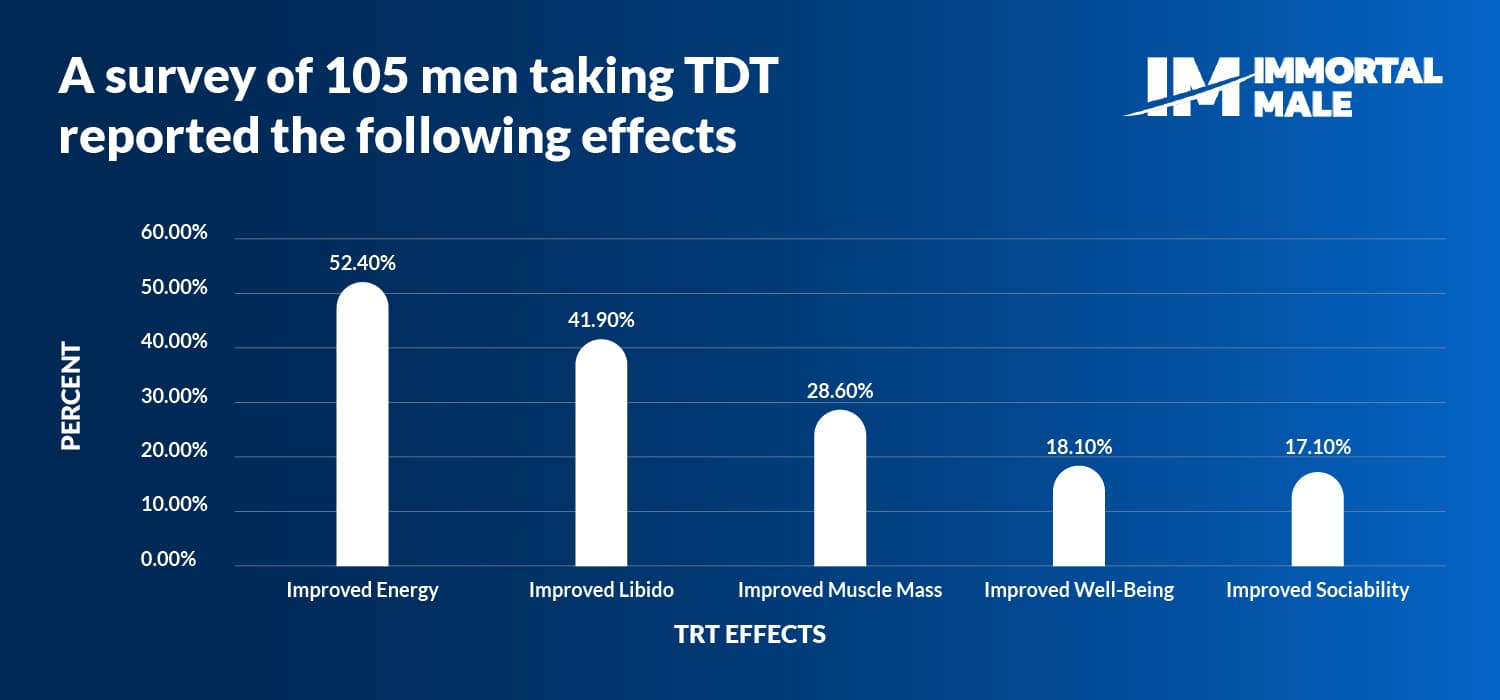
The benefits of testosterone therapy are numerous. Evidence based benefits of TRT include improved libido and erectile function, improved mood and energy, and improved muscle mass and strength to name a few.25
Testosterone’s effect on the body has been proven to increase lean muscle mass, decrease fat mass, and increase bone density and strength. In a review of multiple studies on the impacts of TRT on patient strength, it was found that lower extremity strength increased by more than 10% in patients receiving intramuscular injections of testosterone.31In a study on improvements to bone strength following testosterone treatment for 12 months, it was found that spine trabecular bone strength also improved by an estimated 10.8%.32
A meta-analysis of TRT’s effect on patient management of major depressive disorder found that TRT had a significant positive effect in patients diagnosed with both major depressive disorder and hypogonadism.33

Are you looking to learn more about what is considered low testosterone and how to get started on treatment?
Immortal Male is a premier testosterone replacement therapy center. The TRT program offered by Immortal Male is designed to assist patients with achieving healthy testosterone levels. It also works to address other common concerns, such as hair loss or high cholesterol.
Immortal Male places patient health and comfort first and foremost. Patients will find that they are in the care of a highly educated team prepared to answer any of the questions that arise during the treatment process. Call us today to learn what is considered low testosterone and how you can overcome these issues.
Immortal Male is an online clinic that helps men optimize their hormones.
As part of your membership and as medically indicated, physicians prescribe medications, and recommend supplements that are delivered to you from the comfort of your home.